
Normal Variants in theChest
Adam Guttentag M.D.
Albert Einstein Medical Center
Philadelphia, PA







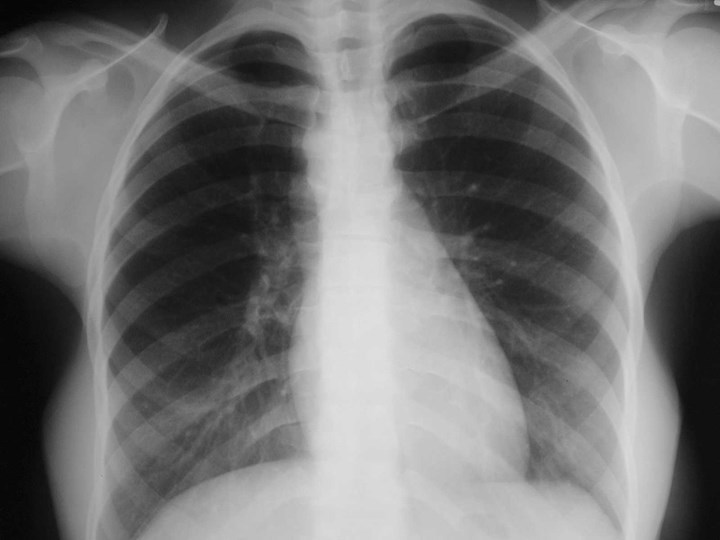
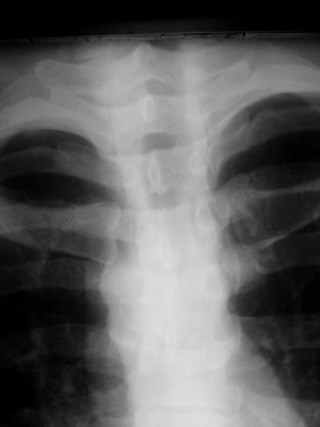

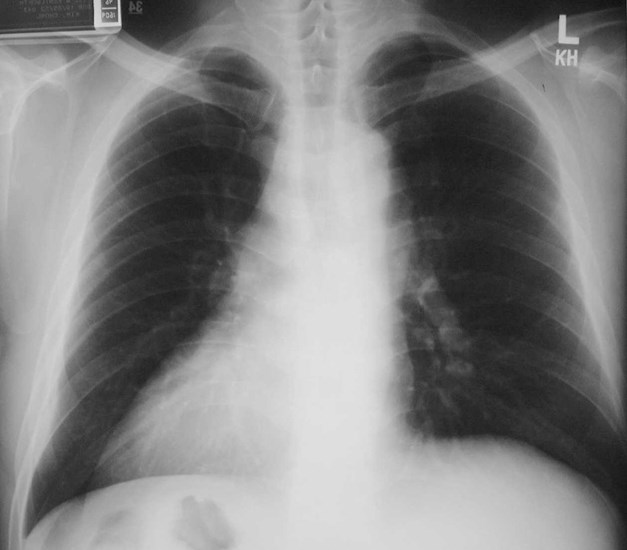

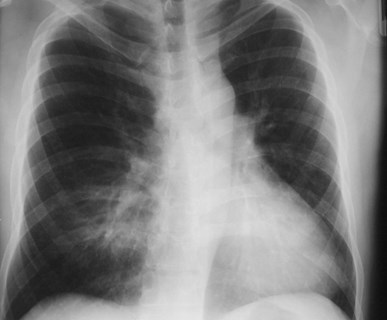

Normal

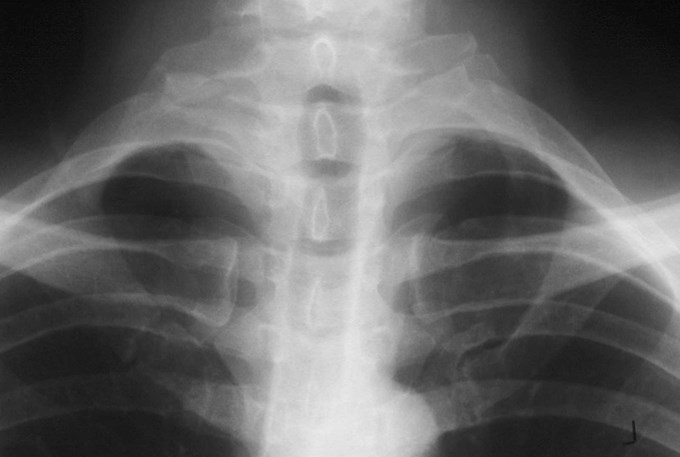
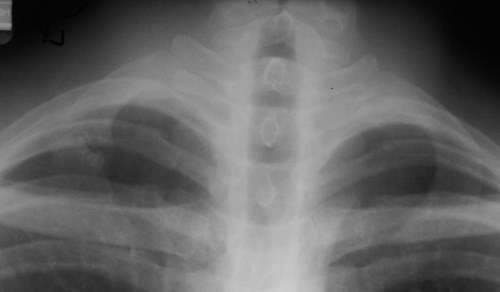
Cervical rib
•Up to 8% incidence
•variable size
•may articulate with 1st rib
•usually Asx
•may cause “mass” or thoracic outletsyndrome

What if computer error messageswere in haiku form?

Windows NT crashed.
I am the Blue Screen of Death.
No one hears your screams.

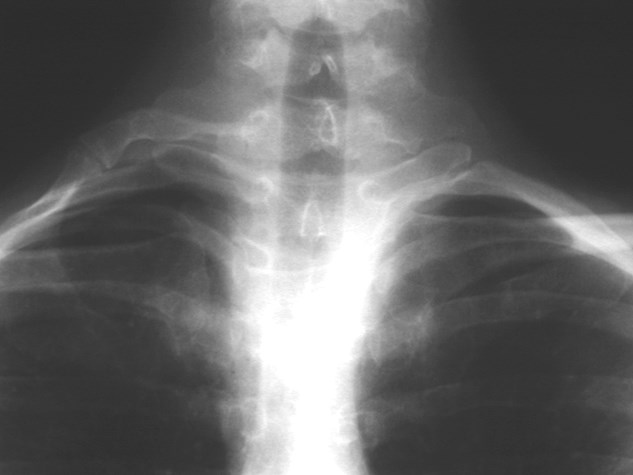
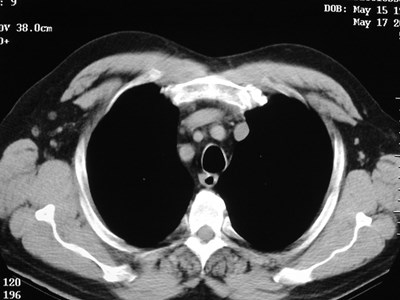
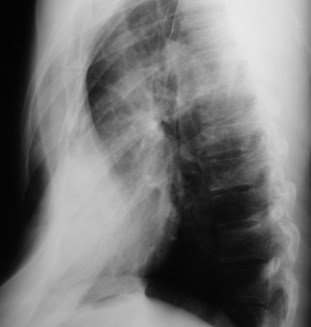
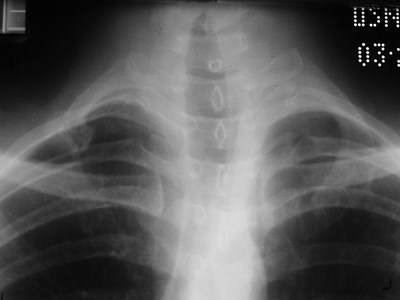
Cervical rib with pseudoarticulation with 1st rib

T1

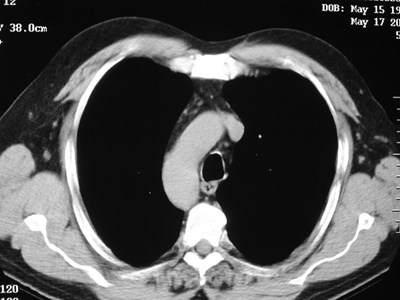
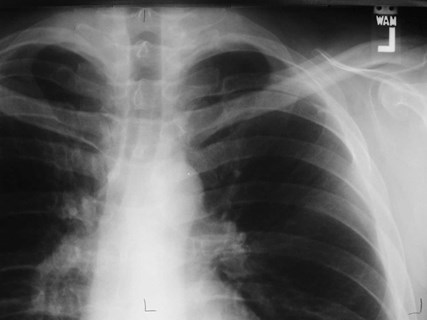
Bony bridging of ribs

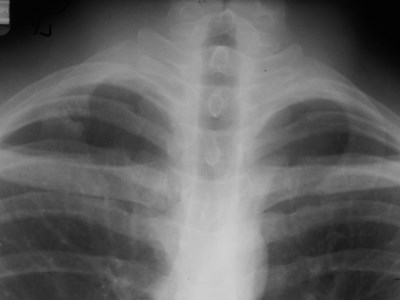
Pseudo-fracture of 1st rib

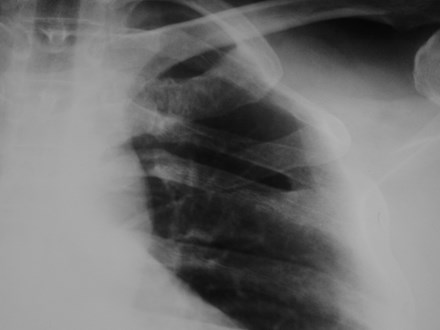
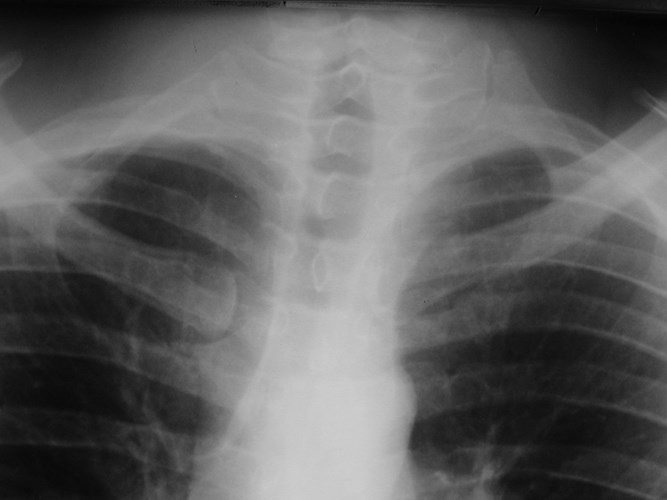
Fused ribs

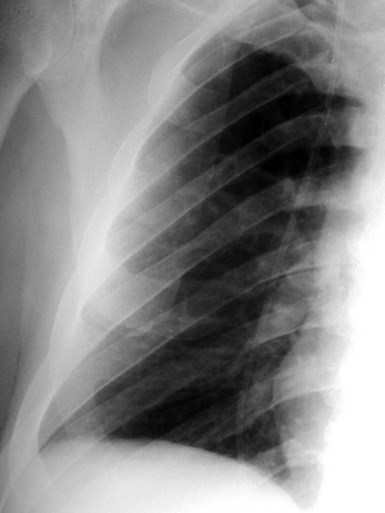



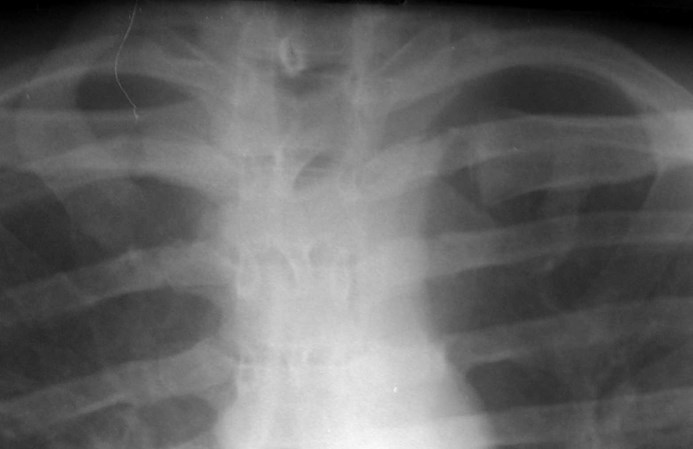


1st rib absent except for cartilage

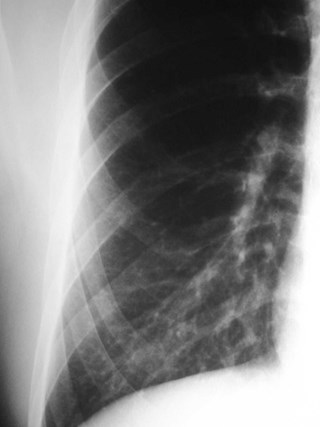
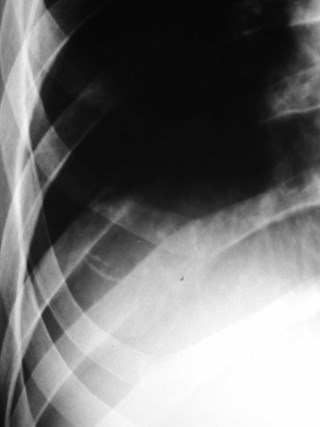
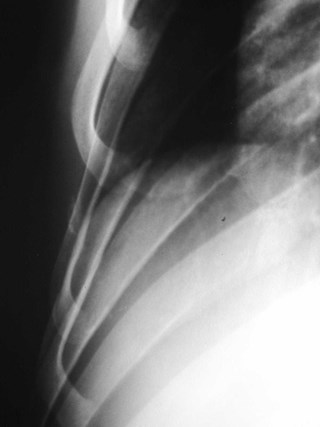



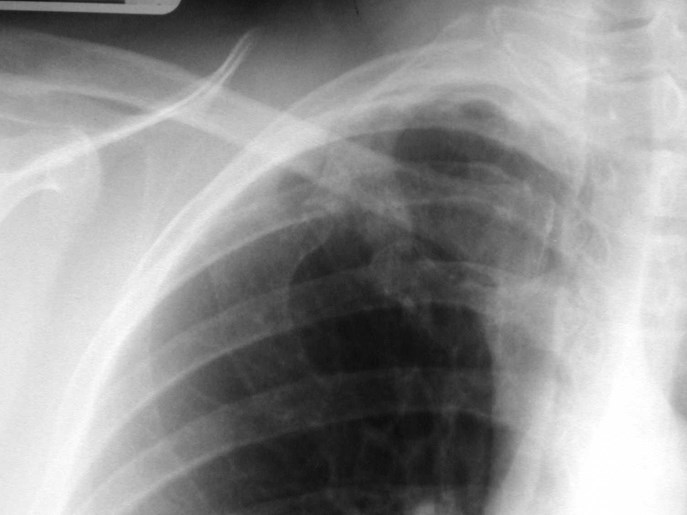
Rhomboid fossa
•Attachment of costoclavicular ligamentsconnecting 1st rib to clavicle
•may simulate lung disease


Yesterday it worked.
Today it is not working.
Windows is like that.




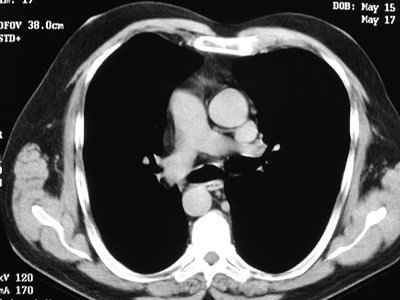
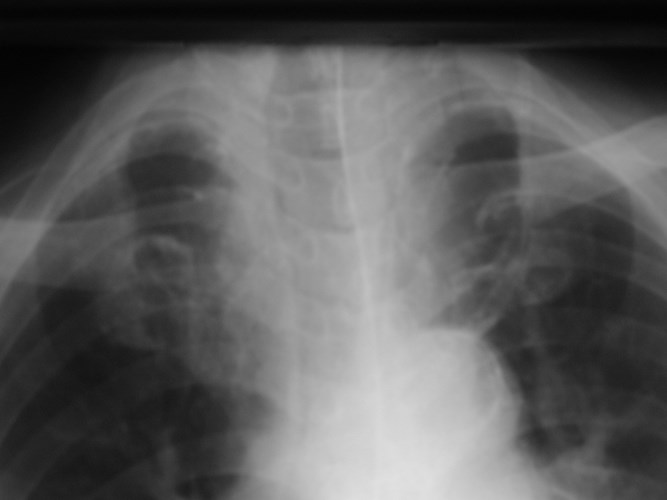
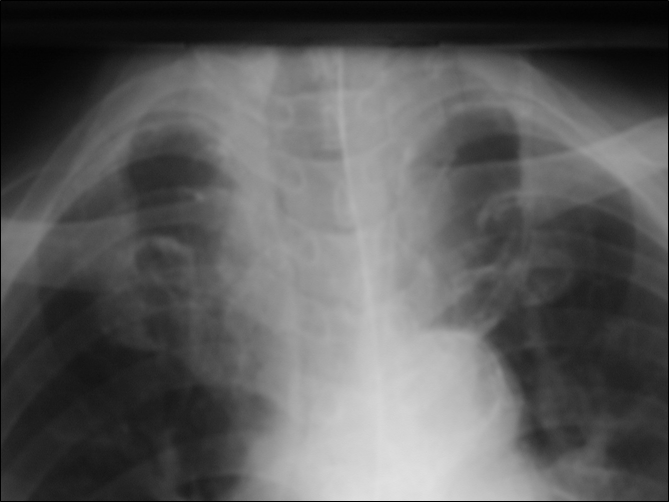
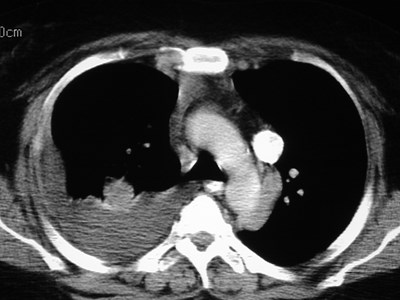
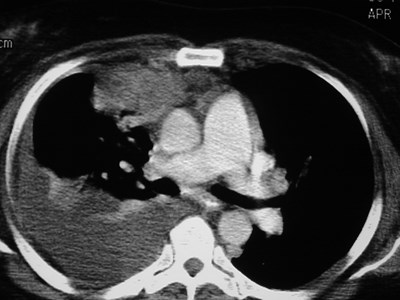
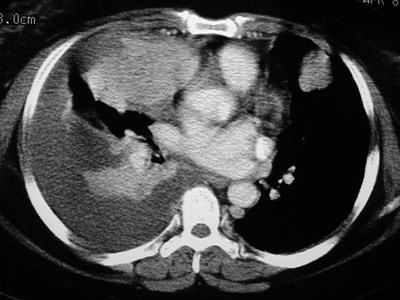
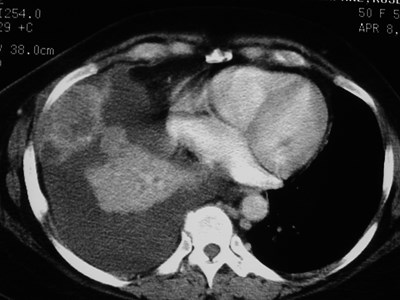
Left SVC
•Found in 0.4% of normal patients
>4% of patients with CHD
•May be solitary (85%) or with separateright SVC
•empties into right atrium via coronarysinus
•differentiate from anomalous pulmonaryvein (“vertical vein”)


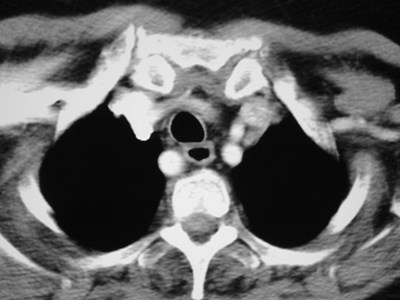
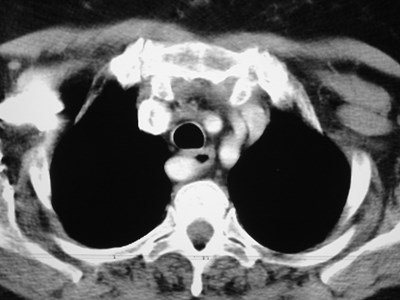
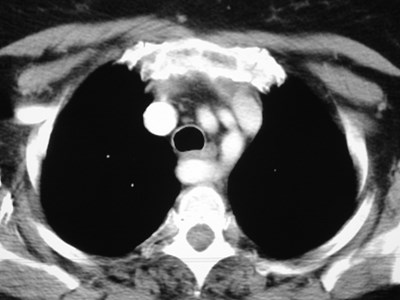
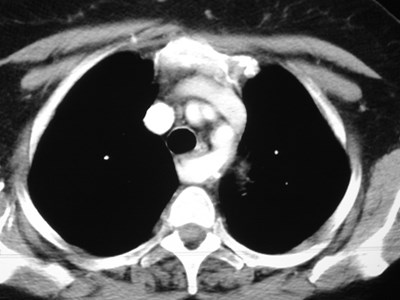

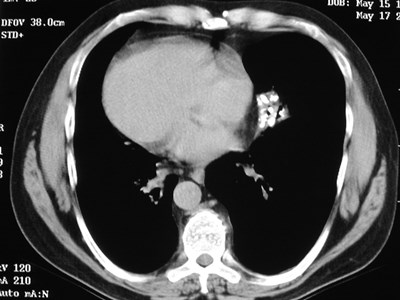
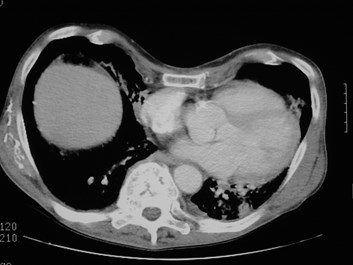
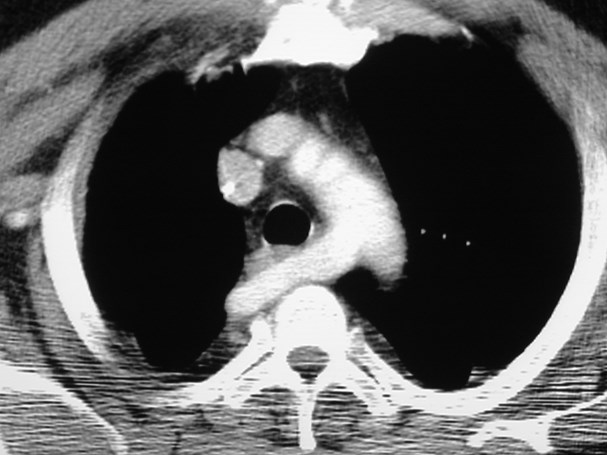
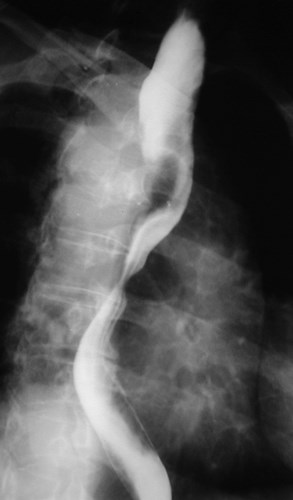
Aberrant right subclavian artery
•Incidence 0.5%
•dilated origin known as diverticulum ofKommerell
•usually asymtomatic
•courses behind trachea and esophagus


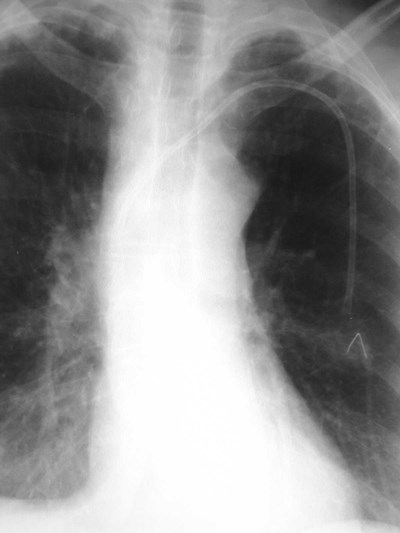
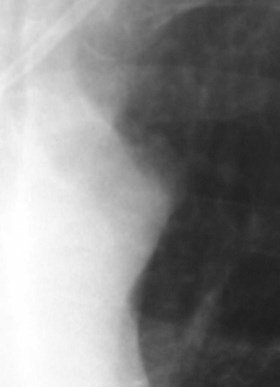

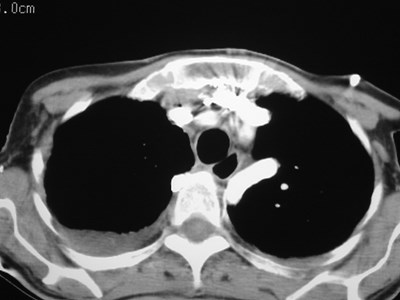
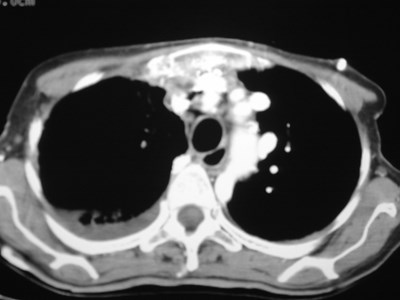
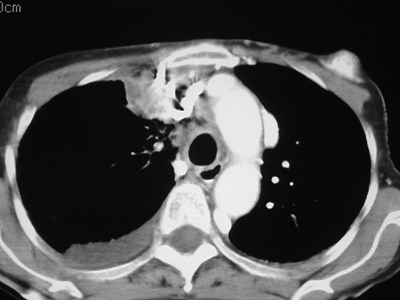
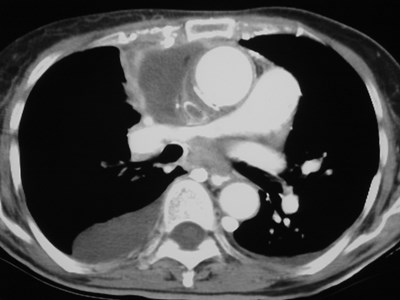

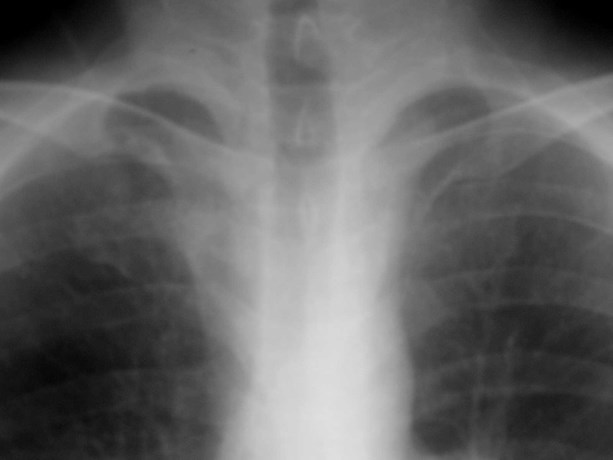
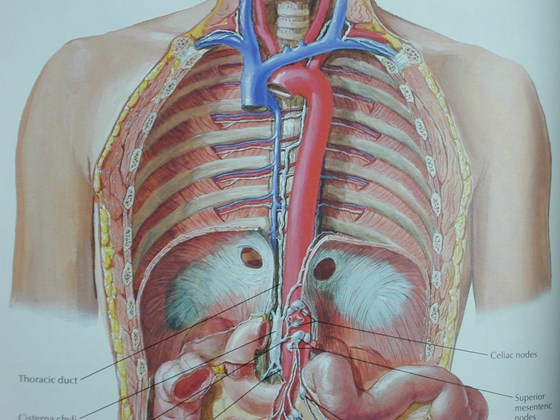
Superior Intercostal Vein
•aka “aortic nipple”
•left sided homologue of azygos arch
connects hemiazygos system with leftsubclavian vein
•pathway of collateral flow withobstructed SVC or LBCV


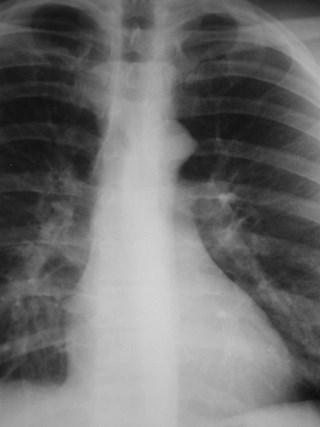
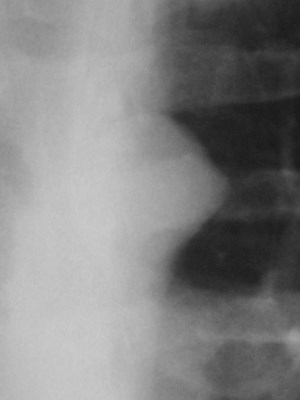

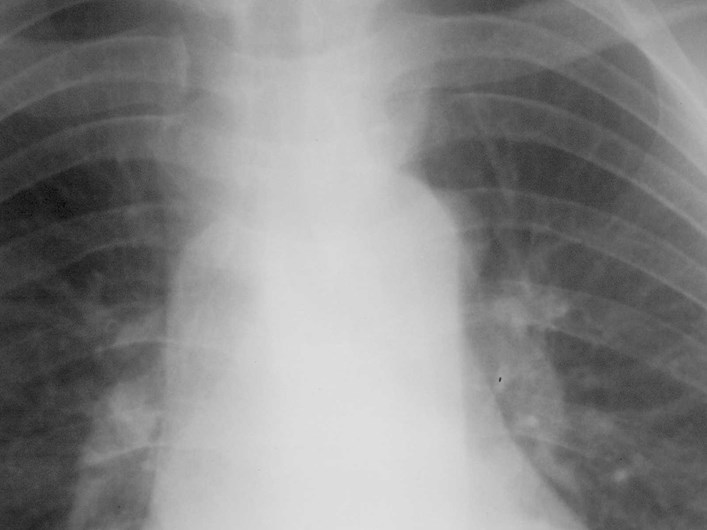

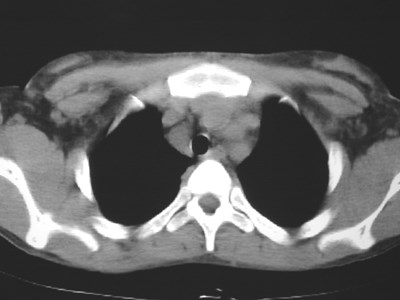
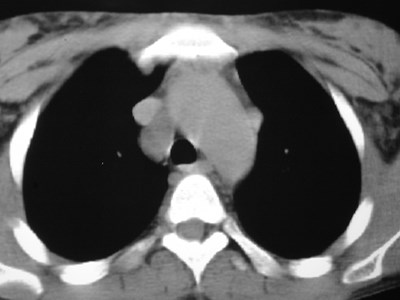
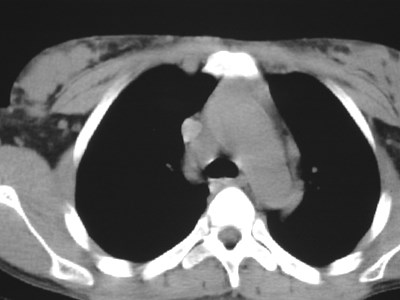
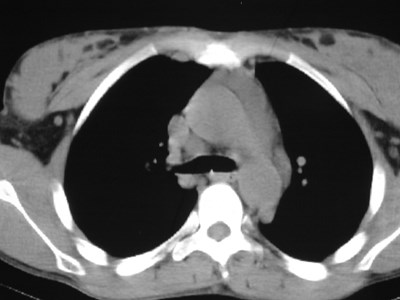


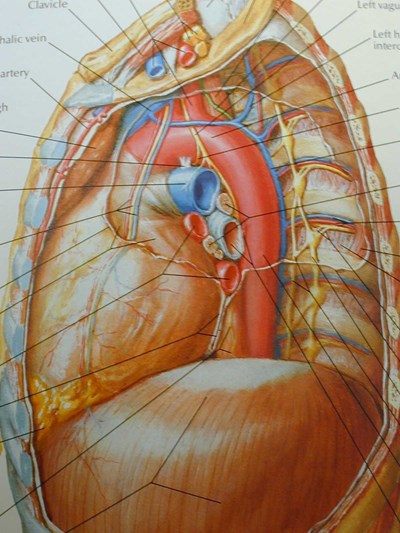
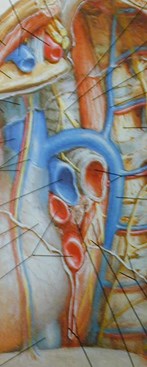

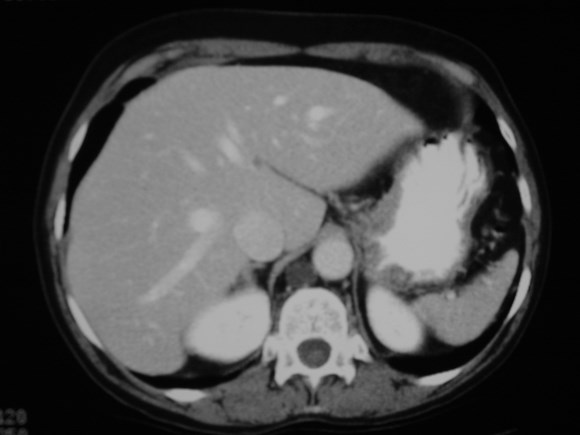
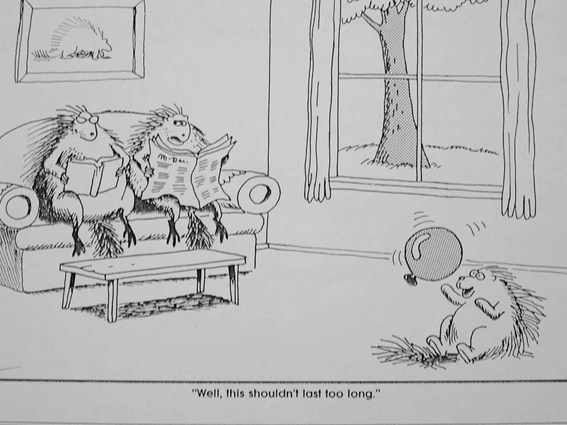
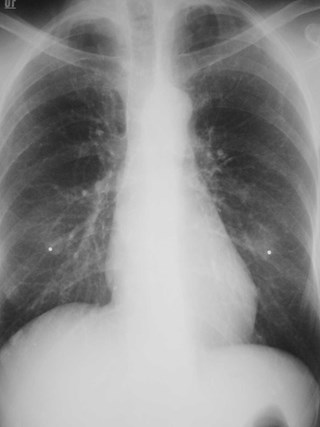
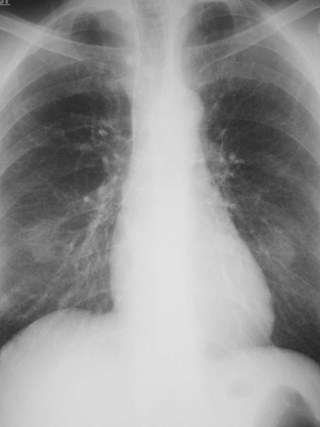
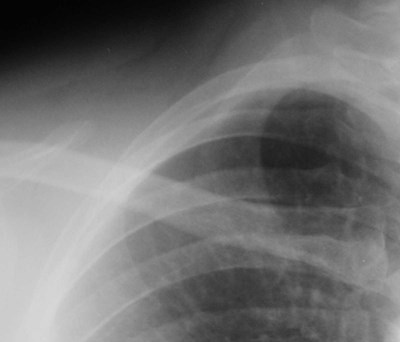
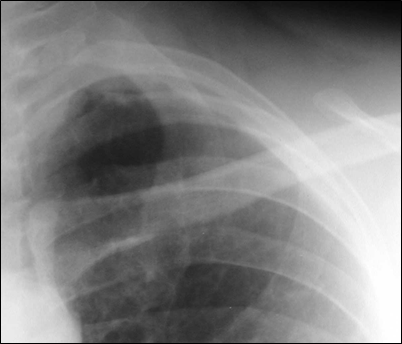
Lung cancer. ?mets



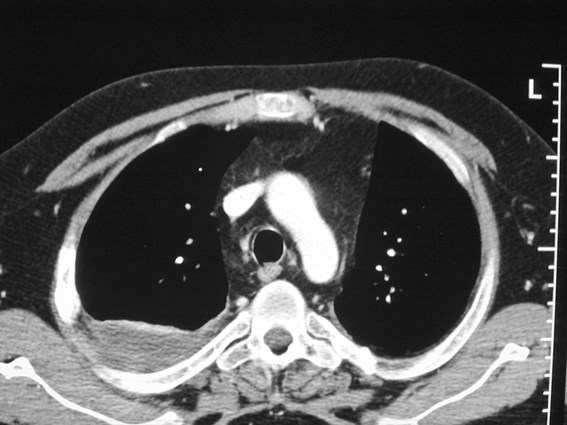

Three things are certain.
Death, taxes and lost data.
Guess which has occurred.

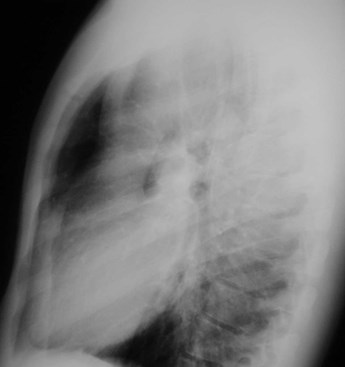
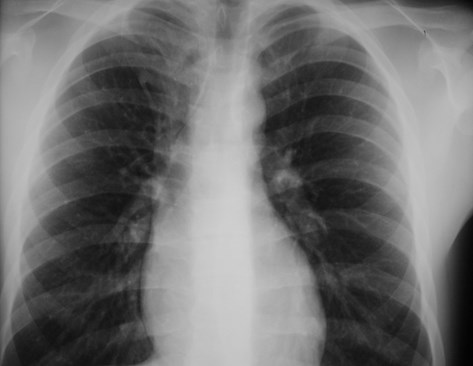
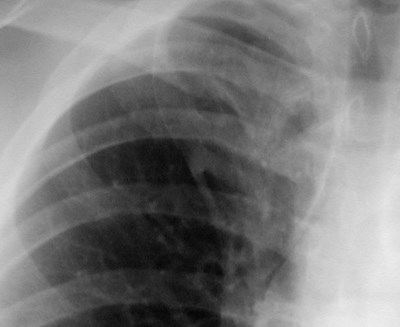

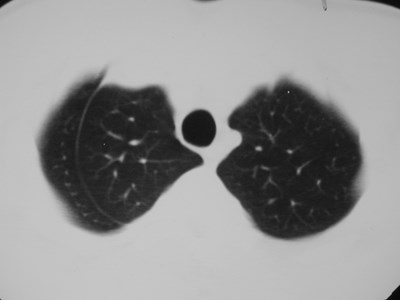
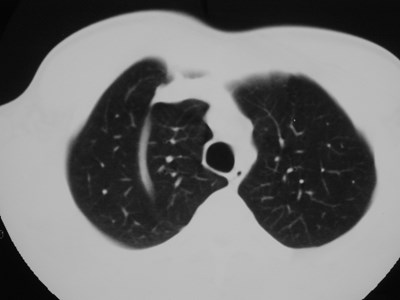
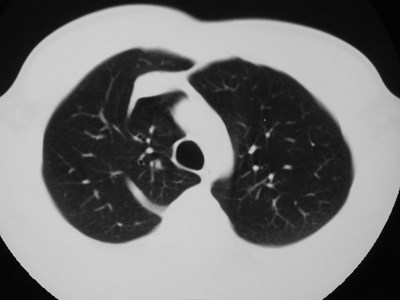
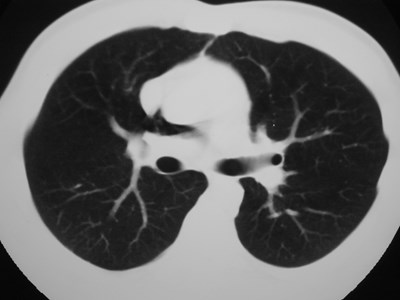

Accessory fissures
•Present in up to 50% of lungs
•Vary from superficial slits to completefissures extending to hilum
•May limit spread of disease process inunusual ways
•Mostly of academic interest:
Recognize and ignore!

Azygos fissure
•Invagination of azygosvein into RUL
•Only accessory fissureto have both visceraland parietal pleura (2layers each)
•Variable amount ofRUL isolated
•Azygos vein visible asteardrop shapednodule at the end ofthe fissure
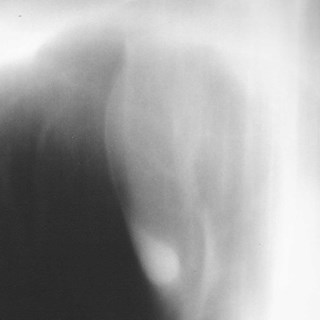

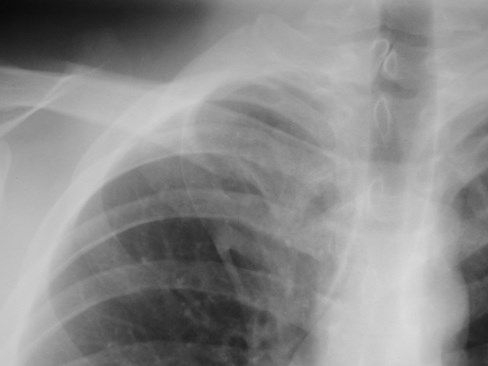
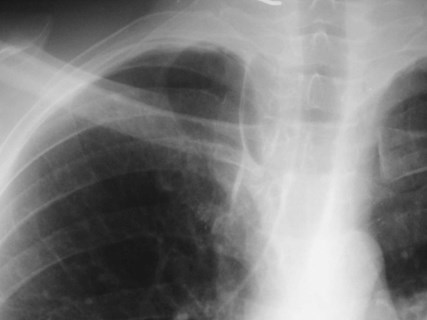

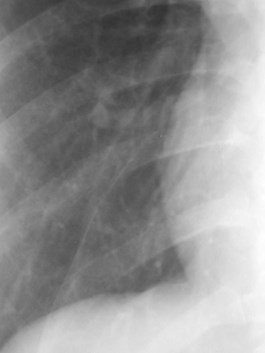
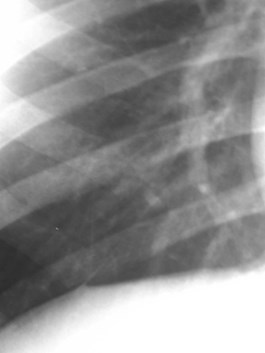
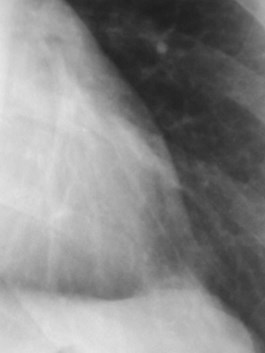

Inferior Accessory Fissure
•Either lower lobe
•More common on right
Seen to some degree in 45% at autopsy
Seen radiographically in 8%
Seen more commonly on CT - 16%
•Separates medial basal segment fromthe rest of the lower lobe basalsegments

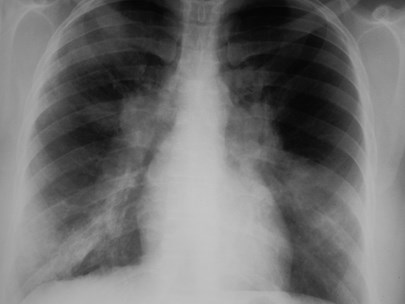
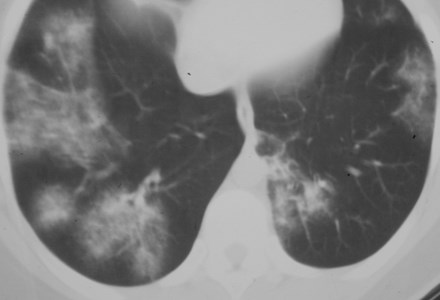
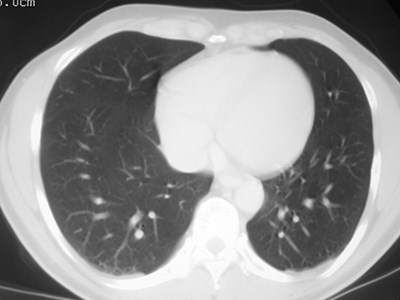
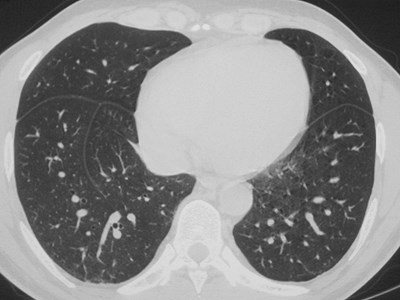

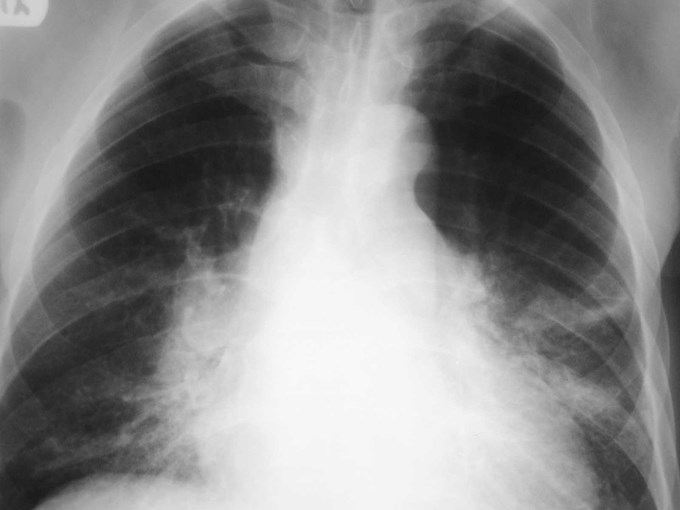
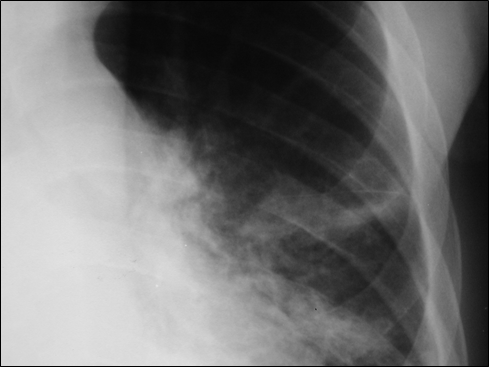

Left minor fissure
•Separates lingular segments from therest of the LUL
•2-8% of CXR’s

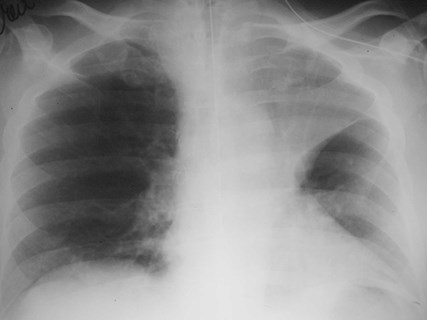
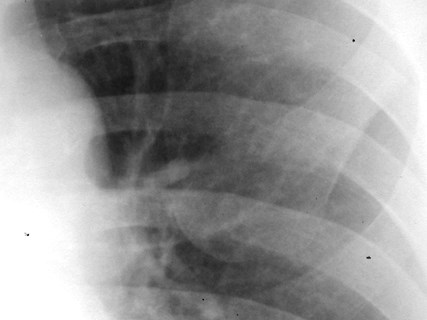
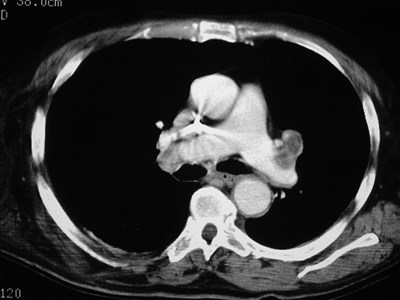

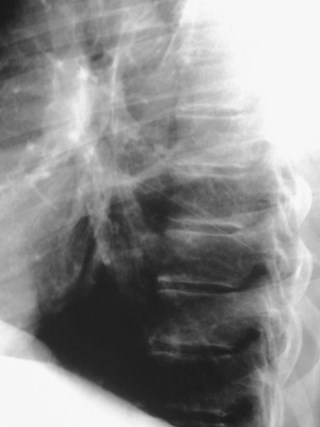
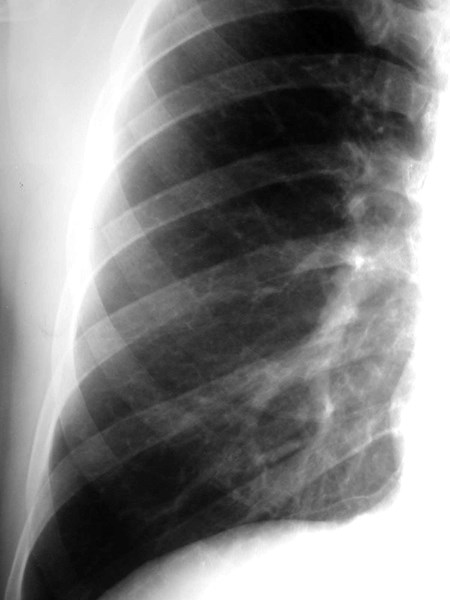

Superior Accessory Fissure
•Separates superior segment fromremained of lower lobe
•Found on both sides
•More common on right

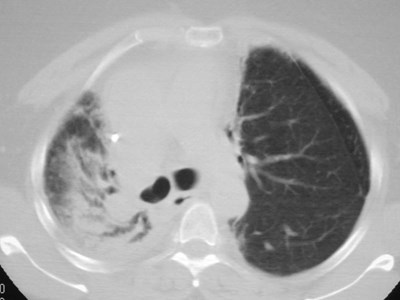
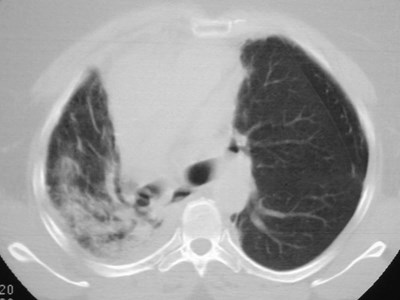
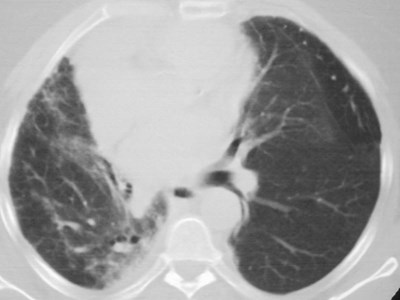
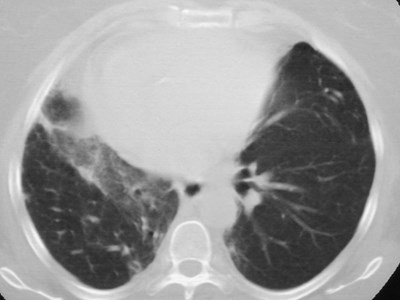
Accessory fissure LUL

Your file was so big
It must have been quite useful
But now it is gone.

